Introduction
The application of growth hormone (GH) transgenesis technology in fish has led to significant growth improvement as an effect of overexpression of the inserted GH gene (Hinits & Moav, 1999; Mori & Devlin, 1999; Nam et al., 2001). Transgenesis of GH causes excessive fish growth that is several times higher than that of non-transgenic fish, having the potential to increase fish culture yields. The growth of transgenic mutiara catfish (inserted CgGH sequence, GenBank accession no.MN249238.1) reported by Buwono et al. (2016; 2019b; 2021) was high (2–3 times that of non-transgenic fish) because of exogenous GH (CgGH) insertions at G0, G1, G2, and G3. This inserted transgene was successfully inherited in three generations through the reproduction of transgenic broodstock with CgGH transmission rates of 42.85% in G1, 50% in G2 and 70% in G3 (Buwono et al., 2021). Transgene inserts integrated into the fish genome have been shown to be inheritance on to offspring through broodstock reproduction. Some examples include studies on trout showing the inheritance of pSV518 in G2 by 49%–75% (Tewari et al., 1992). Transmission of the antifreeze protein gene (AFP) that was inherited in G2 by the transgenic G1 Atlantic salmon broodstock pair following Mendel’s law by 50% showed stable inheritance in the transgenic salmon generation (Hew et al., 1992). The percentage of transgene transmission from crosses of G1 transgenic and non-transgenic Nile tilapia fish (Oreochromis niloticus) ranged 49%–52% which is consistent with Mendelian inheritance (Rahman & Maclean, 1999). Transgene inheritance of 50% from the broodstock to the offspring of this transgenic fish possible it to be transmitted to the offspring through the reproduction of the broodstock fish.
Based on the alignment of CgGH sequences from transgenic mutiara catfish, G0, G1, G2, and G3 can exhibit sequence similarities among all four generations, reflecting the consistency in CgGH inheritance in each generation (Degani et al., 2006; Pinheiro et al., 2008; Rajesh & Majumdar, 2007). Confirmation of the presence of CgGH in G1, G2, and G3 transgenic mutiara catfish broodstock to ensure transgene transmission in each reproductive offspring. It is important to evaluate the similarity of functional domains of CgGH sequences in the offspring of this transgenic catfish to achieve mass production of transgenic catfish lines. The similarity of functional domains in the CgGH sequence may indicate the similarity of the GH protein molecules formed between the four generations of transgenic mutiara catfish.
Materials and Methods
Fish used this study were kept at the Aquaculture Laboratory Universitas Padjadjaran in circular tanks containing 1,000 liters of freshwater. Fish were adapted to 12 hours’ daylight photoperiod conditions. Rearing conditions were kept at optimal water quality which were 27 ± 1°C, pH 6–6.5 and optimal dissolved oxygen (continuous aeration). As much as 10% of water was replaced with freshwater while in the same time faeces and feed left over were siphoned. All fish were daily fed with commercial feed (Hiprovite 781) with the dose of 3% total biomass. Fish used for the research were the G0 ♀broodstock (weighing 1,600 g, total length of 58 cm and age of 12 months), G1 ♀ broodstock (weighing 1,200 g, total length 55 cm and age of 12 months), G2 ♀ (weighing 950 g, total length of 50 cm and age of 11 months), G3 ♀ (weighing 910 g, total length of 46 cm and age of 11 months).
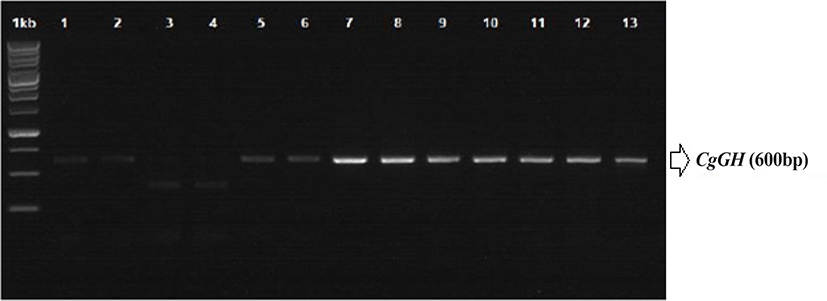
RNA was isolated from 10 mg of fish tail fin tissue of G0, G1, G2, and G3 was isolated using the RNeasy mini kit (Qiagen, Venlo, Netherlands), following the kit instructions for RNA isolation. Sampling was carried out on the tail fin of the broodstock, not taken from gonadal tissue or liver because the broodfish was used for the production of the next generation. Transgenes (including CgGH) can be inserted in fish tissues along the head to tail region (Rahman & Maclean, 1999; Uh et al., 2006). Synthesis of cDNA and RT-PCR (semi-quantitative PCR) of CgGH were performed using My Taq OneStep RT-PCR (Bioline, London, UK) with the following cycling programme: 48°C for 20 min; 40 cycles of 95°C for 1 min, 95°C for 10 s, 60°C for 30 s and 72°C 30 s; and 72°C for 5 min. Confirmation of transgenic catfish was achieved by detecting the presence of a PCR product of approximately 600 bp using primers GH-F (5΄-ATGGCTCGAGTTTTGGTGCTGCT-3΄) and GH-R (5΄-CTACAGAGTGCAGTTGGAATCCAGGG-3΄) (Buwono et al., 2021; Zhang et al., 2009).
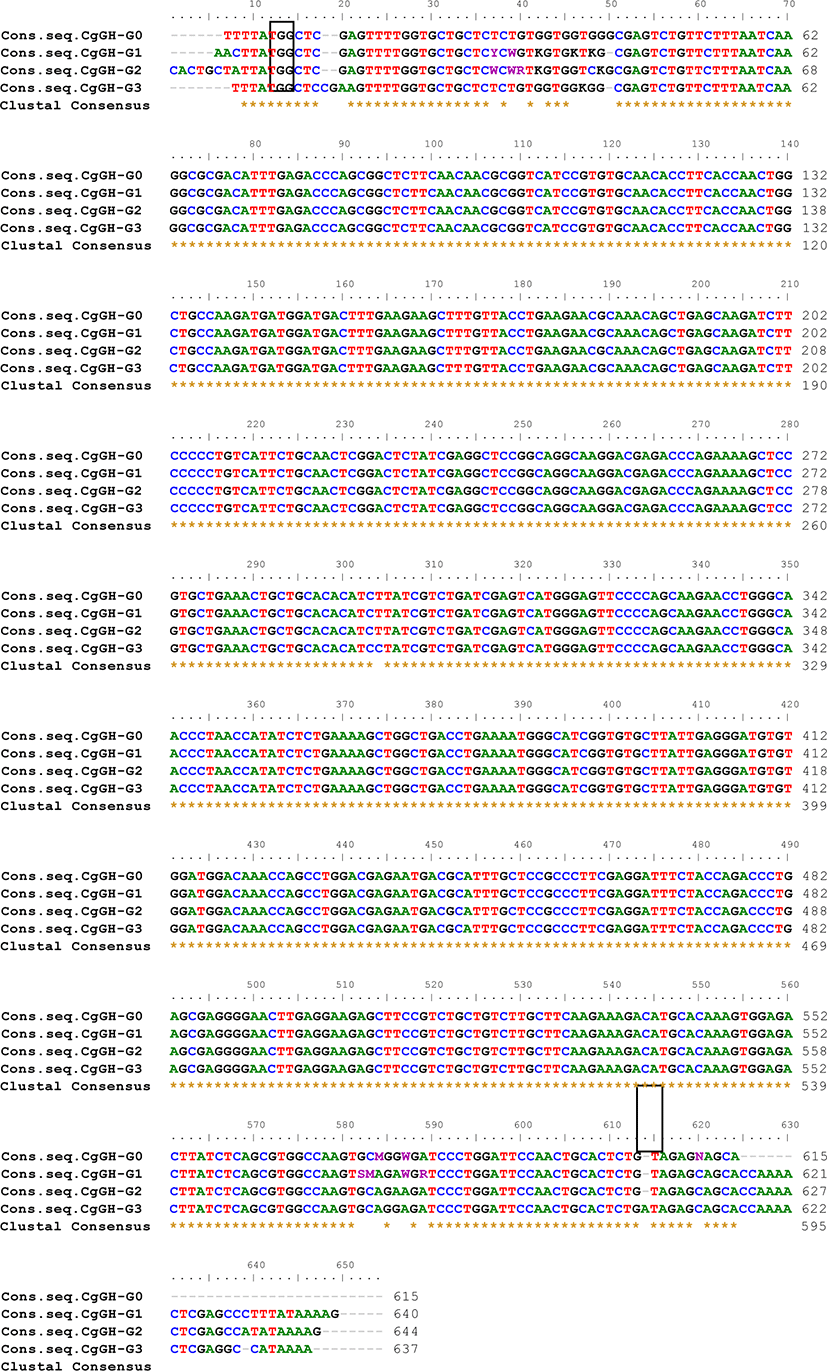
The CgGH gene amplicon (PCR product of G0, G1, G2 sample A and B, G3 sample A, B, and C) was then sequenced using the Sanger sequencing method through service 1st BASE (Molecular Biology Company) Singapore because the amplicon size is less than 1,200 bp (Sanger et al., 1977). Nucleotide sequence similarity analysis of the CgGH gene in G0, G1, G2, and G3 transgenic mutiara catfish was performed using the BioEdit 7.0.5.3 software (http://www.mbio.ncsu.edu/BioEdit/BioEdit.html) to identify the consensus sequences of the four CgGH inserts in the generations of transgenic catfish. To the CgGH nucleotide similarity analysis, we used the consensus sequence, to equate the complementary sequence from the forward direction, so that this consensus sequence could be used to CgGH sequence similarity analysis to G0, G1, G2, and G3 as written in Table 1 and Fig. 2.
| Nucleotide (nt) | CgGH-G1 (%) | CgGH-G2 (%) | CgGH-G3 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CgGH-G0 | 93.76 | 93.78 | 95.15 |
| CgGH-G1 | 97.06 | 96.42 | |
| CgGH-G2 | 96.29 |
The presence of CgGH in transgenic catfish was confirmed by aligning the gene sequence with the Clarias gariepinus GH coding sequence (cds) in GenBank to determine the similarity of the nucleotide base sequences encoding the fish GH protein (Peyush et al., 2000). CgGH nucleotide base sequence similarity among the generation of transgenic mutiara catfish was identified using the BLAST (Basic Local Alignment Search Tools) programme (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/BLAST/). The functional domains of CgGH sequences, especially amino acid residues, were analysed using SWISS-MODEL (https://swissmodel.expasy.org/) to map the molecular structure of fish GH protein.
Results
ThePCR analysis results showed that CgGH was amplified using the primers GH-F and GH-R in the test samples G0, G1, G2, and G3 and had a size of approximately 600 bp (Fig. 1). The size of this amplified sequence was also not markedly different from that of the Clarias gariepinus GH sequence in GenBank (accession nos. EF411172 and MN249238.1), with sizes of 603 and 615 bp, respectively. This indicated that the CgGH gene sequence present in the four generations of transgenic mutiara catfish is the GH gene of C. gariepinus. Consensus sequence analysis results of the four generations of transgenic mutiara catfish also showed high nucleotide similarity of CgGH consensus sequences (Table 1 and Fig. 2).
Considering that G0 transgenic mutiara catfish is a germline transmitter and G1 fish is produced from a transgenic × non-transgenic cross, functional domain analysis of CgGH (forward direction) was conducted between G2 transgenic mutiara catfish resulting from crossing A (sample A coded 1st_BASE_3044995 and sample B coded 1st_BASE_3044997) (Buwono et al., 2019a) with G3 transgenic mutiara catfish sample A (transgenic female-1 × transgenic male-1), B (transgenic female-2 × transgenic male-2) and C (transgenic female-3 × transgenic male-3) (Buwono et al., 2021) using the Sanger method for the sequence process while the alignment used the CLUSTALW BioEdit software. The results of the analysis showed that the CgGH gene sequences (forward direction) of thw G3 fish (samples A, B, and C) with G2 fish showed high similarity (96.21%, 96.38%, and 95.91%, respectively).
Differences in CgGH nucleotides between G2 (code 1st_BASE_3044995 sample A) and G3 fish sample A (1st_BASE_3527728_A) occurred of 16 nucleotides in the first sequence, and in nucleotides 594, 597, 600, 606 and 610 (Fig. 3A). At nucleotide numbers 594, 597, and 600 of G2 fish there was a lack of cytosine, thymine and cytosine residues, and at nucleotide 606 of G3 fish, there was a lack of thymine residue. The start codon (ATG) and stop codon (TAG) were located at nucleotides 18–20 and 576–578, respectively. In G3 fish of sample B (1st_BASE_3527730_B), there was a difference of 16 nucleotides in the first sequence of CgGH with G2 fish (code 1st_BASE_3044997 sample B). In G3 fish, nucleotides 600–602 lacked three thymine residues and nucleotide 609 lacked a guanine residue (Fig. 3B). The start codon, ATG, was located at nucleotides 17–20, and the stop codon, TAG, at nucleotides 575–577. The results of the alignment of the CgGH sequence of G2 fish (code 1st_BASE_3044995 sample A) with that of the G3 fish of sample C (1st_BASE_3527732_C) showed a difference of 14 nucleotides in the first sequence, where the start codon was located at nucleotides 18–20 and the stop codon at nucleotides 571–573 (Fig. 3C). In sample G3, nucleotides 600, 601, 604, and 608 lacked adenine, thymine, adenine and guanine residues, respectively. The amino acid residues in Figs 3A–C are underlined and marked with coloured boxes after conversion using SWISS-MODEL to form a three-dimensional structure of the GH protein molecule.
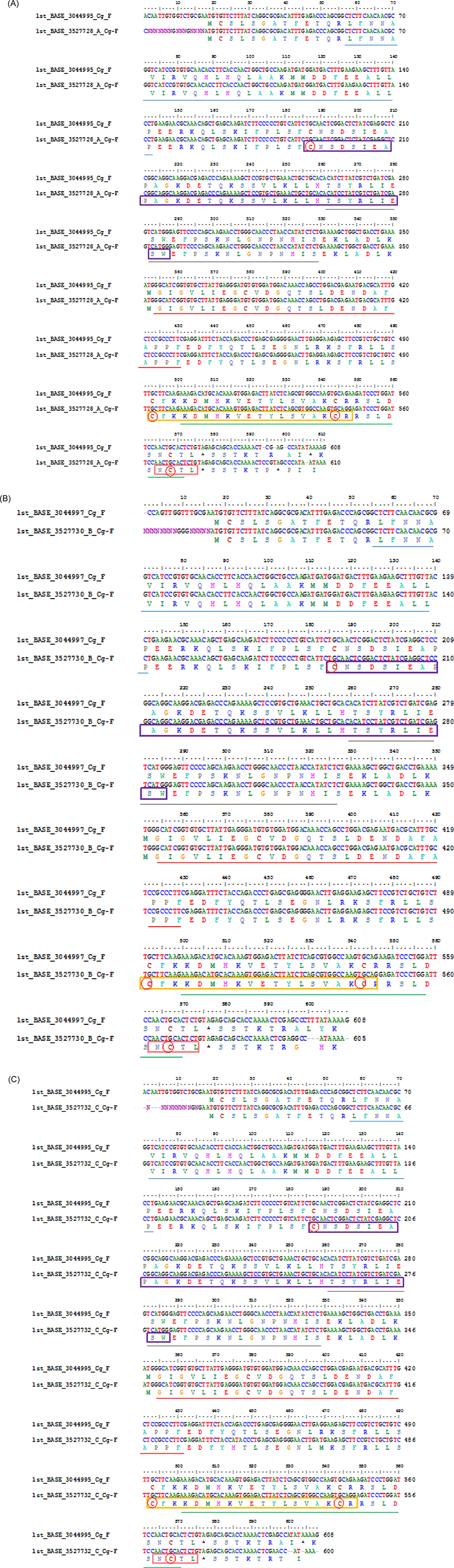
Overall alignment of the sites of somatotropin-1 (nucleotide 186–287), somatotropin-2 (nucleotide 492–548), N-glycosylation (nucleotide 564–575), 4-residue cysteine (nucleotide 181, 493, 544, 598), helix -1 (nucleotide 56–143), helix-2 (nucleotide 261–329), helix-3 (nucleotide 354–431) and helix-4 (nucleotide 501–572) were contained in the CgGH sequence in both G2 of sample A (1st_Base_304495) and G3 fish sample A (1st_BASE_3527728_A) were located on the same nucleotide (nt.) (Fig. 3A). Meanwhile, the alignment of the CgGH functional domains between in G2 of the sample B (1st_Base_3044997) and the G3 fish sample B (1st_Base_3527730) were located on different nucleotides. In G2 of the sample B, the somatotropin-1 site at nt. 186–286, somatotropin-2 at nt. 491–547, N-glycosylation at nt. 563–574, 4-cysteine residue at nt. 186, 492, 543, 562, helix-1 at nt. 56–141, helix-2 at nt. 260–328, helix-3 at nt. 353–430 and helix-4 at nt. 500–574, while in G3 of the sample B, the somatotropin-1 site at nt. 187–287, somatotropin-2 at nt. 492–548, N-glycosylation at nt. 564–575, 4-cysteine residue at nt. 187, 493, 544, 563, helix-1 at nt. 57–142, helix-2 at nt. 261–329, helix-3 at nt. 354–431 and helix-4 at nt. 501–575 (Fig. 3B). The alignment of the position of the CgGH functional domain between in G2 of the sample A (1st_Base_3044995) and the G3 fish sample C (1st_Base_3527732) was also located on different nucleotides. Somatotropin-1 (nt. 187–287), somatotropin-2 (nt. 492–548), N-glycosylation site (nt. 564–575), 4-cysteine residue (nt. 187, 497, 544, 568), helix-1 (nt. 57–143), helix-2 (nt. 261–329), helix-3 (nt. 354–431) and helix-4 (nt. 501–572) in G2 of the sample A, while in G3 fish sample C is located at different nucleotides, namely somatotropin-1 (nt. 183–283), somatotropin-2 (nt. 488–544), N-glycosylation (nt. 560–571), 4-cysteine residue (nt. 183, 493, 540, 564), helix-1 (nt. 53–139), helix-2 (nt. 257–325), helix-3 (nt. 350–427) and helix-4 (nt. 493–564) (Fig. 3C).
Discussion
The presence of CgGH in four generations of transgenic mutiara catfish indicates that the exogenous GH gene is inherited stably in each generation of GH-transgenic catfish. The rate of CgGH transmission in G2 transgenic mutiara catfish was 50% and increased in G3 to 70% (Buwono et al., 2021). This indicates the potential for increased CgGH transmission in crosses between G4 transgenic catfish as a consequence of the stability of CgGH inheritance in transgenic catfish offspring. Homozygous transgenic fish need to be produced to obtain stable transgene inheritance (Iwai et al., 2009). Homozygous fish were produced when crossing between heterozygous G2 mud loach (Misgurnus mizolepis) transgenic fish (carrying CMV-H2B-GFP) to produce 50% homozygous G3 progeny (Nam et al., 2000).
To confirm its stable inheritance, the stability of the CgGH sequence needs to be analysed for similarity as an indication that its copies in G0, G1, G2, and G3 transgenic mutiara catfish have high similarities between generations. Yang et al. (2018) also explained that the coding region in the gene sequences are generally conserved and have high similarities with those of related fish species. There was a high homology of the gene encoding the hormone oxytocin, which regulates GH release in ricefield eel (Monopterus albus), being 84.6% identical to that of Anguilliformes (Anguilla bicolor). High homology was shown in the gene sequences encoding GH in C. gariepinus G0 fish compared with those in G1 fish (93.76%), G2 fish (93.78%) and G3 fish (95.15%), indicating that the nucleotide sequence of CgGH did not change much and was conserved (Table 1). In addition, there was a tendency for an increase in the homology of CgGH sequences between G1 and G2 and G3 fish by 97.06% and 96.42%, respectively. The results of another study also indicated that the GH sequences of blue gourami (Trichogaster trichopterus) and pearl gourami (T. leeri) showed high homology as conserved sequences, at 97% and 96%, respectively (Degani et al., 2006). The same study also showed that the Indian catfish (Heteropneustes fossilis) GH sequence had high homology (98%) with the Siluridae and Clariidae groups (Anathy et al., 2001). It was shown that the CgGH sequence was conserved with high homology (93.76%–97.06%) in four generations of transgenic mutiara catfish, which was required for stable exogenous GH inheritance in the transgenic fish generations. The consistency of CgGH consensus sequence homology in G0, G1, G2, and G3 fish, especially at the start codon (ATG) and stop codon (TAG), is shown in Fig. 2, indicating that the coding sequence of CgGH is conserved in the generation of transgenic mutiara catfish.
Functional domains are conserved sequences that characterise a particular gene group consisting of 40–700 amino acid residues (Xiong, 2006). Generally, five functional domains characterise fish GH sequences (somatotropin-1 and somatotropin-2, N-glycosylation, four α-helix structure and four cysteine residues), which are homologous (Anathy et al., 2001; Pinheiro et al., 2008). The results of SWISS-MODEL processing showed that the four characteristic sites of the GH molecule (somatotropin-1, somatotropin-2, α helix-1 to α helix-4, N-glycosylation and four cysteine residues) in the CgGH sequences of G2 and G3 fish were conserved and located at the same base pairs. According to Anathy et al. (2001) and Pinheiro et al. (2008), α- helix-1 is encoded by amino acid residues LFNNAVIRVQHLHQLAAKMMDDFEEALLP (underlined in blue), α helix-2 by TSYRLIESWEFPSKNLGNPNHIS (underlined in gold), α helix-3 by GIGVLIEGRVDGQTSLDENDAFAPPF (underlined in red) and α helix-4 by KDMHKVETYLSVAKCRRSLDSNCT (underlined in green). These four helix structures are bound by four cysteine residues (marked with red circles). The α-helix site is a domain that indicates the formation of a secondary structure of GH protein, namely, α-helix sites 1 to 4, which are important for the functional activity of these hormones (Pinheiro et al., 2008). Generally, this domain has relatively high homology among the GH of freshwater fish (including the catfish group). The amino acid residues CNSDSIEAPAGKDETQKSSVLKLLHTSYRLIESW (marked with purple box) are the functional domain of somatotropin-1, and the amino acid residues CFKKDMHKVETYLSVAKC (marked with yellow box) are the functional domain of somatotropin-2. The existence of these two functional domains is related to GH activity and synthesis of insulin-like growth factor-1and prolactin for tissue growth. The somatotropin sites (1 and 2) present in the GH sequences of transgenic mutiara catfish (G2 and G3) and in Indian catfish (Anathy et al., 2001) are both conserved. N-glycosylation site domains encoded with NCTL amino acid residues (marked with pink boxes) in GH protein sequences were also found to be conserved in fish (including transgenic mutiara catfish) and act as signals for protein transport to the cell surface (Degani et al., 2006). Another important site is four cysteine residues (C) in the protein-coding GH gene, which are involved in the formation of two disulphide bonds for the structural integrity and biological activity of the hormone (Anathy et al., 2001); the five functional domain sites were found to be conserved in CgGH of G2 and G3 transgenic mutiara catfish (Figs 3A–C). The molecular structure of GH protein in G3 mutiara catfish (samples A–C), shown in Fig. 4A–C, was confirmed as a GH protein molecule (Swiss model analysis), as shown in the Siluriformes group GH protein molecule (Vaz et al., 2010).
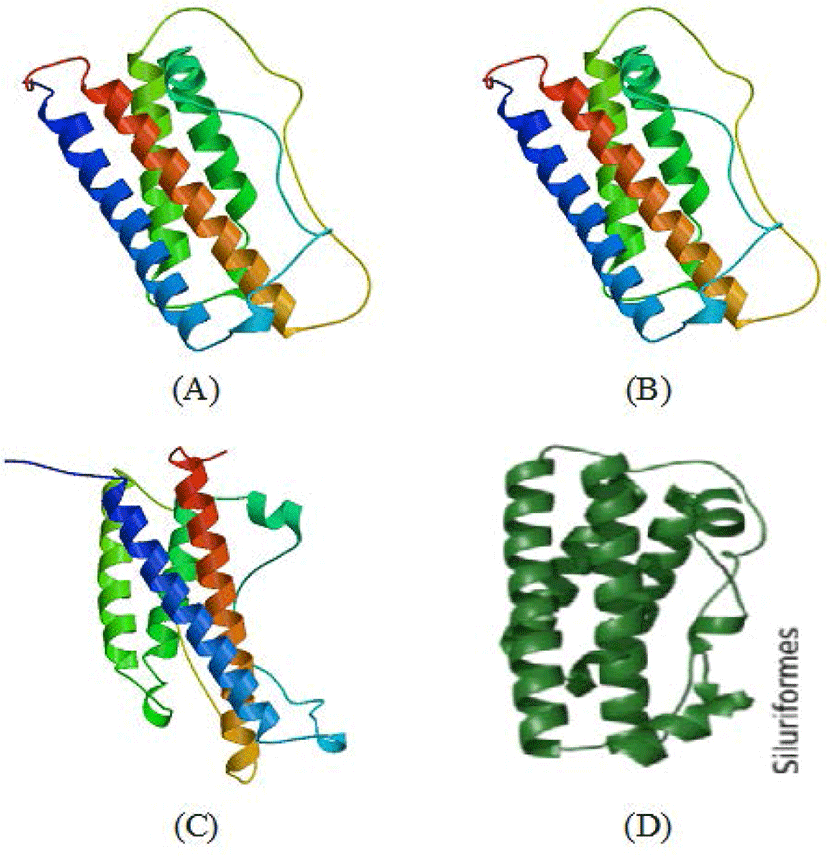
These results indicate that CgGH from Gs broodstock had been successfully inherited in up to three generations (G1, G2, and G3) with a high degree of similarity and confirmed as fish GH protein. This verification was based on analysis of the functional domains of fish GH molecules composed of somatotropin-1 and somatotropin-2, four-helix structures, N-glycosylation and four cysteine residues that bind to the helix structure (Pinheiro et al., 2008; Vaz et al., 2010).
Conclusion
CgGH (600 bp) can be inherited in G1, G2, and G3 transgenic mutiara catfish through reproduction. The consensus sequence similarity of CgGH between transgenic fish in G1 to G3 ranged from 93.76% to 97.06%, and they had five fish GH protein functional domain sites (somatotropin-1, somatotropin-2, four α-helix, N-glycosylation and four cysteine residues).







